Description
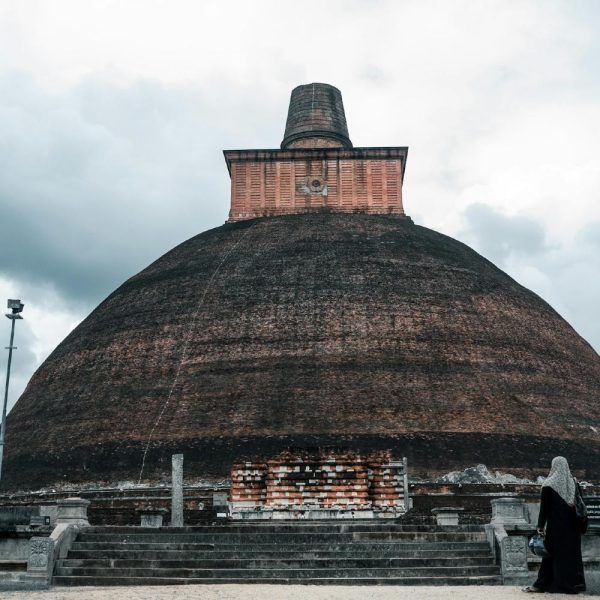
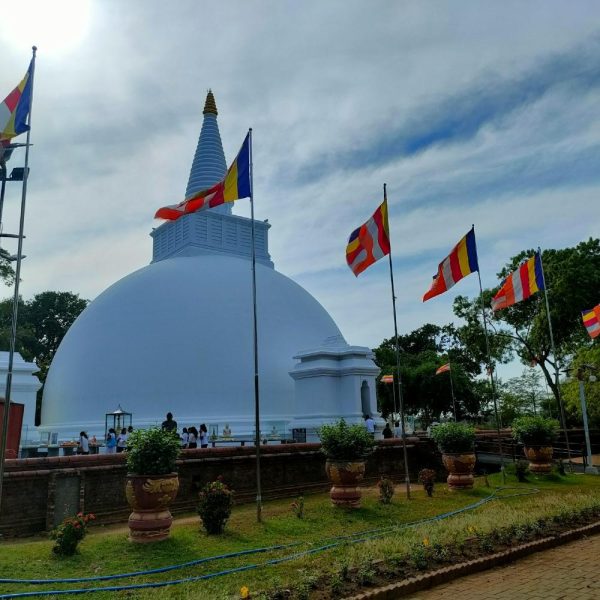
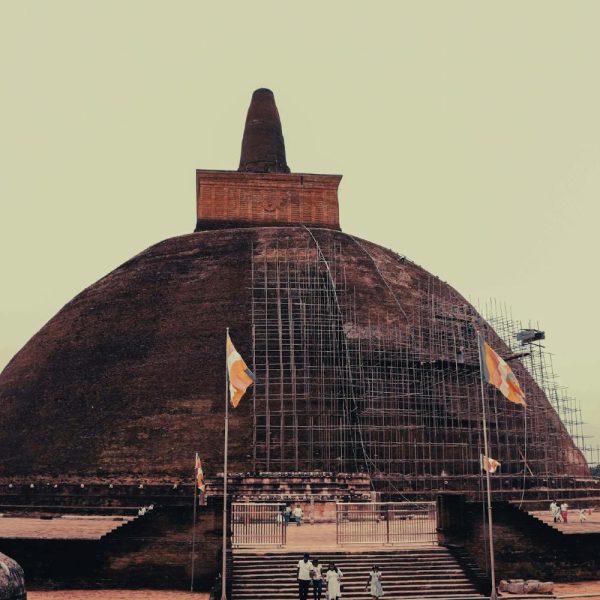
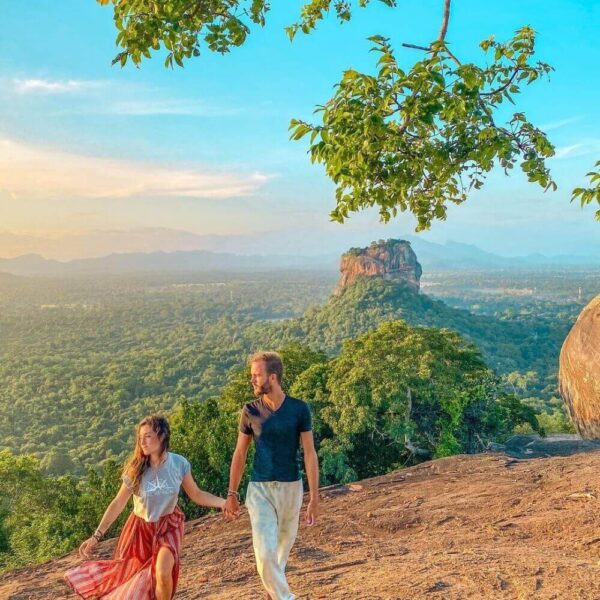
Thuparamaya is a historic Buddhist dagoba (stupa) located in the ancient city of Anuradhapura, Sri Lanka. It holds significant importance as one of the earliest stupas in the country and is considered a sacred site for Buddhists.
Key features and points of interest at Thuparamaya include:
- Oldest Stupa: Thuparamaya is believed to be the oldest dagoba in Sri Lanka, dating back to the 3rd century BCE. It was built during the reign of King Devanampiya Tissa, following the introduction of Buddhism to the island by Arahat Mahinda.
- Shape and Architecture: The stupa has a distinctive bell-shaped design, a common architectural style of ancient stupas in Sri Lanka. The structure is constructed with bricks, and its form represents the early architectural evolution of Buddhist stupas in the region.
- Monastic Complex: Thuparamaya is part of a larger monastic complex, and it includes various structures such as monastic cells, stone pillars, and other archaeological remnants. The site provides insights into the layout of ancient Buddhist monastic establishments.
- Buddhist Relics: Like many stupas in Sri Lanka, Thuparamaya is believed to enshrine relics of the Buddha. The dagoba served as a repository for sacred relics and became a focal point for Buddhist worship.
- Moonstone: The entrance to Thuparamaya features a moonstone, a semicircular stone carving with intricate patterns representing various aspects of Buddhist cosmology. Moonstones are a characteristic feature of ancient Sinhalese architecture.
- Vatadage: Thuparamaya is surrounded by a vatadage, a circular relic house that once housed the stupa. The vatadage is adorned with guard stones, balustrades, and other decorative elements.
- Devotional Area: The premises of Thuparamaya are considered sacred, and visitors engage in religious activities such as making offerings, circumambulating the stupa, and participating in rituals.
- Archaeological Significance: Thuparamaya, along with other monuments in Anuradhapura, is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site due to its historical and cultural significance.